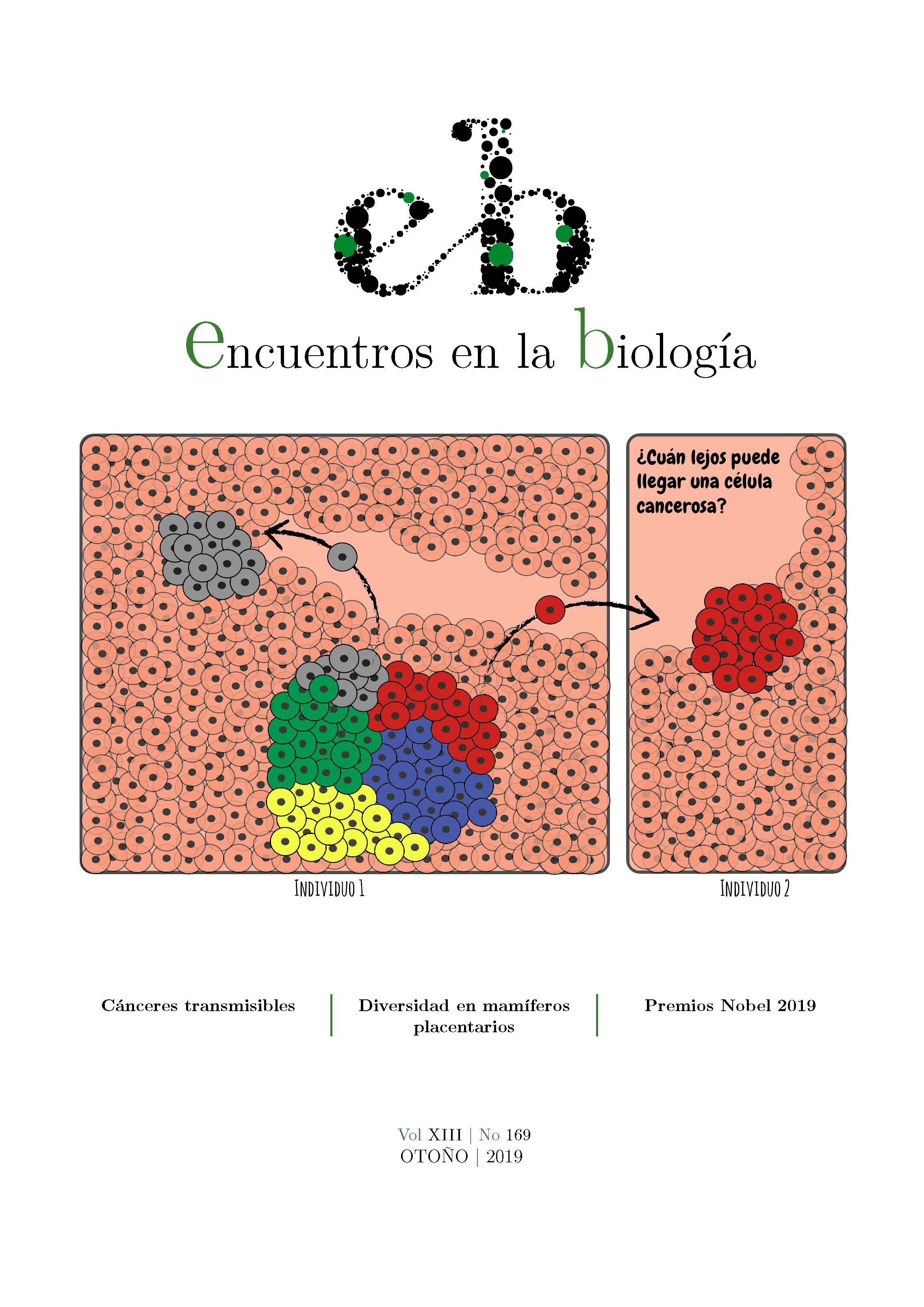
The enemy of my enemy is my friend
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24310/enbio.v13i169.17465Keywords:
microbiome, biocontrol, network analysisAbstract
Plants health is influenced by the characteristics of the plant, the environment, specially the soil, and the microbiome associated with them. The study of the interaction networks of the different components of the microbiome can provide strategies for the development of a sustainable agriculture as well as being environmental friendly
Downloads
Metrics
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
Indexed in
-
—
- Academic society
- N/A
- Publisher
- Uma Editorial. Universidad de Málaga
References
Melcher U, Verma R y Schneider WL. Metagenomic search stra- tegies for interaction among plants and multiple microbes. Front. Plant. Sci. 5:268, 2014.
Hunter P. Plant microbiome and sustainable agriculture. EMBO reports 17(12): 1696-1699, 2016.
Rossman M, Sarango-Flores SW, y otros. Plant microbiome: composition and functions in plant compartments. En The Brazilian Microbiome. V. Pyro, L. Roesch (eds). pp 7-20, 2017.
van der Heijden, MGA y Hartmann, M. Networking in the plant microbiome. PLOS Biol. 14: e1002378, 2016.
Agler TA, Ruhe J, y otros. Microbial hub taxa link host and abiotic factors to plant microbiome variation. PLoS Biol 14(1):e1002352, 2016.
Poudel R, Jumpponen A y otros. Microbiome networks: a systems framework for identifying candidate microbial assemblages for di- sease management. Phytopathol. 106(10): 1083-1096, 2016.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Esta obra está bajo licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
Esta revista provee acceso libre inmediato a su contenido bajo el principio de hacer disponible gratuitamente la investigación al público. Todos los contenidos publicados en Encuentros en la Bilogía están sujetos a la licencia Creative Commons Reconocimento-NoComercia-Compartirigual 4.0 cuyo texto completo puede consultar en <http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0>
Se pueden copiar, usar, difundir, transmitir y exponer públicamente, siempre que:
Se cite la autoría y la fuente original de su publicación (revista, editorial y URL de la obra).
No se usen para fines comerciales.
Se mencione la existencia y especificaciones de esta licencia de uso
Los derechos de autor son de dos clases: morales y patrimoniales. Los derechos morales son prerrogativas perpetuas, irrenunciables, intransferibles, inalienables, inembargables e imprescriptibles. De acuerdo con la legislación de derechos de autor, Encuentros en la Biología reconoce y respeta el derecho moral de los autores/as, así como la titularidad del derecho patrimonial, el cual será cedido a la Universidad de Málaga para su difusión en acceso abierto. Los derechos patrimoniales, se refieren a los beneficios que se obtienen por el uso o divulgación de las obras. Encuentros en la Biología se publica en open access y queda autorizada en exclusiva para realizar o autorizar por cualquier medio el uso, distribución, divulgación, reproducción, adaptación, traducción o transformación de la obra.
Es responsabilidad de los autores/as obtener los permisos necesarios de las imágenes que están sujetas a derechos de autor.
Los autores/as cuyas contribuciones sean aceptadas para su publicación en esta revista conservarán el derecho no exclusivo de utilizar sus contribuciones con fines académicos, de investigación y educativos, incluyendo el auto-archivo o depósito en repositorios de acceso abierto de cualquier tipo.
La edición electrónica de esta revista esta editada por la Editorial de la Universidad de Málaga (UmaEditorial), siendo necesario citar la procedencia en cualquier reproducción parcial o total.