The purpose of this paper is to analyze whether family influence impacts on the degree of utilization of the management control systems (MCS), and the relationship between the former and performance. To this end, this study was carried out using a sample of 900 Spanish SMEs, both family and non-family businesses. The findings show that family businesses use less management control systems than non-family firms and that the use of MCS has a positive influence on business performance. This study is useful for firm managers and practitioners as it can encourage them to develop systems that allow control of the firm direction and improve the firm's competitiveness.
El objetivo del presente trabajo es analizar si existen diferencias entre la empresa familiar y no familiar en cuanto al grado de utilización de los Sistemas de Control de Gestión (SCG) y su relación con el rendimiento de la empresa. Para ello se ha llevado a cabo un estudio empírico utilizando una muestra de 900 pequeñas y medianas empresas españolas, familiares y no familiares. Los resultados muestran que las empresas familiares hacen un menor uso de los SCG que las empresas no familiares y que el uso de los SCG influye positivamente en el rendimiento empresarial. Este trabajo resulta de utilidad a los directivos y consultores de las empresas para que desarrollen sistemas que permitan controlar la gestión de la empresa y mejorar su competitividad.
The complexity and dynamism of today's business environment requires a thorough knowledge of the organizations and the variables or factors that may be considered key to competitive success. MCS become essential for decision making of the company and can be considered a sustainable competitive advantage, if they are correctly developed and structured (Barney, 1991). Financial planning, cost accounting systems or economic and financial diagnosis, among others, should be common tools in organizational systems of all companies regardless of their size. Business managers should base their decisions on objective data, and these can only be obtained if the company uses different economic techniques that are available. However, numerous studies have shown that the use of management control systems is not widespread enough in family businesses. A variety of empirical studies have found that there are differences in the implementation of the MCS between family and non-family businesses that need further research (Kotey, 2005; Laitinen, 2008). In fact, family influence is an important and distinct factor that has not been sufficiently considered by most MCS studies (Senftlechner, Martin, & Hiebl, 2015) and relatively few studies on MCS make the distinction between family and nonfamily firms (Helsen, Lybaert, Steijvers, Orens, & Dekker, 2016).
Likewise, there is growing interest in analysing the relationship between the use of management control systems (MCS) and performance of companies (Bisbe & Otley, 2004). Implementation of MCS also plays an important role in the firm performance, as MCS become key tools that managers should take to planning, budgeting, analysing, measuring and evaluating useful information for proper decision making (Cosenz & Noto, 2015; Dávila & Foster, 2005; Duhan, 2007). Information and planning systems are useful management tools for achieving the strategic objectives of the company (Duhan, 2007), generate creative innovation and achieve the balance between control and flexibility (Simons, 1995).
The aim of this paper is to analyze the degree of utilization of MCS of the family business and its relationship with performance. We have defined MCS as management tools that allows planning, budgeting, analysing, measuring and evaluating the accounting and financial information (Dávila & Foster, 2005). Likewise, a company was considered a family business whether a respondent – the manager – believes the firm is an FB and more than 50% of the capital is in the hands of a family. Finally, firm performance is measured through the perception of managers regarding the competitive position of their firms. To that end, we have conducted a survey on a sample of 900 Spanish SMEs, both family and non-family ones. Then, our main research questions are: are there significant differences in the implementation of MCS between family and non-family firms? Can the MCS help the competitive success of the businesses?
This work has been developed within the framework of the Contingency Theory and the Theory of Resources and Capabilities (Chenhall, 2003; Otley, 1980; Tiessen & Waterhouse, 1983), contributing with new empirical evidence to the body of literature regarding the family influence in the use of MCS. Therefore, we integrate family influence in theory development and control for family influence in an empirical study, as Senftlechner et al. (2015) suggested. This manuscript also highlights the need for businesses to establish mechanisms for management control to achieve the right balance of growth and profitability, and showing the importance of using MCS to improve firm performance.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: first, we review previous empirical literature in the theoretical framework, defining the hypotheses to be tested; secondly, we present the methodology, sample characteristics and justification of the variables used; thirdly, we perform the analysis of the results, and finally, the main conclusions reached.
Theoretical framework and hypothesesManagement control systems and the family firmThe likely involvement in management of family members and the consequent trust within the management team (informal organization), family firm long-term orientation and emphasis on non-financial goals, may influence on the choice of MCS (Senftlechner et al., 2015).
Hopper, Tsamenyi, Uddin, and Wickramasinghe (2009) have shown that family firms consider the use of informal and subjective management controls as the prevalent system of MCS. Informal and family-based controls usually remain well-established throughout the organization's operations (Ansari & Bell, 1991) and MCS are often used only for internal interests (family members) (Uddin, 2009). Family firms often utilize informal communication channels in order to build a familiar surrounding for the communication of the culture and values of the family (Helsen et al., 2016).
Management control systems may also be used to transmit and strengthen the culture of family businesses through the organization and strategically for decision-making (Flamholtz, 1983). The relationship between culture and MCS are two fold that, once created, might have an impact on the way the company values are changed; this means that culture is something that may be handled by the company during its passage through time (Herath, Herath, & Abdul Azeez, 2006). A family firm's focus on the long-term plans, instead of short-term training for employees, enhances the family's SEW, by inculcating the norms and values of the firm in the new employees (Gomez-Mejia, Cruz, Berrone, & De Castro, 2011).
In a study of 536 family and non-family businesses from the United States, Zahra, Hayton, and Salvato (2004) examined the relationship between four dimensions of corporate culture and entrepreneurship. The results showed a positive relationship between strategic control systems of the family business and entrepreneurship, indicating the importance of a long-term oriented culture. However, they also evidenced that financial control systems are mainly focused toward the short-term. Similarly, in a qualitative research with four case studies of Spanish family businesses, Ferna¿ndez and Bringmann (2009) analyzed the organizational culture and leadership styles as factors behind the success or failure of family businesses. Their results revealed that founders are devoting special attention to the implementation of management control systems as tools that contribute to the growth of successful businesses. In addition, they are also paying attention to human resources. In that sense, partners involved in the construction of some strategies enable competitive advantages over other companies with a conservative culture.
With a sample of Spanish family and non-family firms, Duréndez, García Pérez de Lema, and Madrid Guijarro (2007) analyzed the kind of culture, management control systems and performance of these companies, confirming that family businesses have higher hierarchical values and lower values of adhocracy than non-family businesses. Nevertheless, regarding management control systems, the authors suggest that they are used to a lesser extent by family businesses. Likewise, a study of managers of family businesses in Belgium showed that family businesses use the MCS to a lesser extent for several reasons (Jorissen, Laveren, Martens, & Reheul, 2005): first, because of the overlap of the owner–manager relationship and centralized decision-making; secondly, due to the individual authority of the owner, and thirdly, owing to the interaction between the family and the company.
Therefore, generally speaking, previous empirical studies have indicated that family firms are characterized by using the MCS to a lesser extent compared to non-family businesses, giving them a different use (Chua, Chrisman, & Steier, 2003; Kotey, 2005; Laitinen, 2008; Perren, Berry, & Partridge, 1999). Accordingly, we propose the following hypothesis:H1
Family firms use MCS to lesser extent than non-family firms.
Management control systems and performanceAccording to the Contingency Theory, Otley (1980) collected an approximation to the control of management from the Theory of Organizations. Tiessen and Waterhouse (1983) confirmed that the structure of an organization depends on technology and the environment, and they stated that the effectiveness of management processes is a contingent factor affecting the organizational structure. Contingency Theory is based on the fact that the performance of the company depends on the alignment of different organizational factors in a given business situation. In this sense, Chenhall and Langfield-Smith (1998a, 1998b) analyzed the alignment of different variables such as technical accounting control and its impact on business performance. Chenhall (2003) assumed that the MCS should support company managers to achieve organizational goals and benefits, especially when they are well-designed and foster the firm management (Laitinen, 2014). Proper design of MCS will be influenced by certain factors, which the system operates. These factors are: external environment, technology, organizational structure, size, organizational strategy and culture. Abdel and Luther (2008) indicated that MCS should have a high level of sophistication, understood as the organization system capacity to provide leadership, relevant information for planning, monitoring, decision taking, creating and increasing value.
There are a number of reasons why MCS might be beneficial for improving firm performance. Firstly, whether managerial preferences are unstable or objectives cannot be unambiguously codified into quantitative metrics, unproductive discussions from diagnostic mechanisms are likely to happen (Chapman, 1997). MCS enhance mutual commitment and coordinated action toward desired outcomes, foster the definition of goals and their communication, decreasing the uncertainty and leading to higher performance (Adler & Chen, 2011). Secondly, MCS increase the efficiency of locating solutions to task related problems (McGrath, 2001) and put into practice evaluation, improving the performance of groups looking for a solution to problems (Cheng & Van de Ven, 1996).
Regarding MCS and performance, Dávila (2000) related positively the use of the MCS with innovation and company performance. Later, with a sample of Spanish companies, Bisbe and Otley (2004) found that the greater the use of the MCS, the greater the effect of innovation on the performance of small and medium enterprises. With a sample of industrial companies in New Zealand, Adler, Everett, and Waldron (2000) obtained that MCS have a positive influence on product performance. Bright, Davies, Downes, and Sweeting (1992) observed a positive relationship between the development of new cost management techniques and the improvement in product performance. Chenhall and Langfield-Smith (1998a) found evidence of the positive relationship between the use of MCS and performance of companies in Australia. Meanwhile, in a study of small and medium enterprises in Scotland, Garengo and Bititci (2007) provided a comprehensive review of the literature on the main contingent factors that could influence the implementation and use of performance measures in MCS.
Based on the theoretical framework developed in earlier paragraphs and the results achieved in previous studies, this research tests the following hypotheses:H2
The use of the MCS has a positive influence on the performance of family firms.
MethodologyData collection and sampleData was collected through personal interviews with 900 business managers in Murcia (Spain), as a part of a research project called “Barómetro Económico de la Región de Murcia” (Murcia Economic Barometer), promoted and funded by the Instituto de Fomento de la Region de Murcia.1 The sample selection process was designed to characterize the structure of the region following the stratified sampling principles in finite populations. The population of firms was segmented by industry and size. The number of firms in each stratum was implemented according to the information contained in the Companies Registration Office following the criteria of the “Instituto Nacional de Estadística” (Spanish Statistical Office). The selection of companies within each stratum was performed using simple random sampling. Our target population was the number of companies in the Region of Murcia amounting to 95.636 firms (DIRCE, 2010). The Region of Murcia was mainly composed of SMEs (99.92% of the companies, similar to the Spanish national average, 99.90%) (CREM, 2015). The sample selection framework was “Panel Empresarial” (enterprise panel) from the Instituto de Fomento de la Region de Murcia. Firms with fewer than 5 workers were rejected from the study. The estimation of the sample considers in the worst case (relative frequency of answers in a specific item is p=0.5), to a maximum error of 3% at a confidence level of 95%. Companies that chose to not participate in the project were replaced with similar (random election) firms in the same industry and geographic area.
Information was collected through personal interviews with firm managers during April 2009 and July 2009, using a self-managed questionnaire addressed to firm's CEO. SME's managers are the most important decision makers (Van Gils, 2005) and managerial perceptions influence to a significant degree the firm's strategic behavior (O’Regan & Sims, 2008). Control tests were carried out during the elaboration process of the survey. To test for non-response bias, we used late respondents as surrogates for non-respondents (Nwachukwv, Vitell, Gilbert, & Barnes, 1997). Responses of firms answering to the first round of interviews (85% of the sample) were contrasted with those responding to the follow-up (15% of the sample). Then, t-Student and chi-squared tests showed that responses were not significantly different between the two groups for any variable. Considering these outcomes, non-response and industry bias were not found. Likewise, due to the nature of the data, it is possible that the relations between the variables were inflated as a consequence of the common method variance, since the same source is used to gather data for both the dependent and independent variables. We analyzed this bias by the Harman's single-factor test suggested by Podsakoff and Organ (1986). We have realized a factorial analysis including all the dependent variables and independent variables, achieving a unique factor or several factors, which explained a high amount of the variance (Christmann, 2000), in order to confront problems arising from the common method variance in the data. In the factorial analysis executed in our study, six factors were obtained from 22 variables (KMO: 0.841; Bartlett sphericity test Sig. 0.000). These factors explained a 61.865% of the total variance. Between these factors, the first one collects the MCS variables together, and explained a 17.549% of the variance; the second one gathers the financial position variables, explaining 14.581% of the variance. The third one bunches all the performance variables, explaining 11.174%. These results suggested that the bias of the common method variance was not relevant in our study. Nevertheless, it would be important for future studies to check our results using different sources of information for the data.
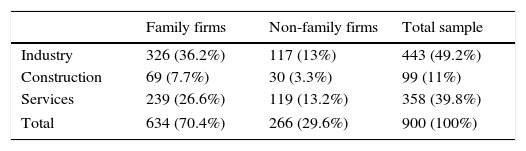
The distribution of responding firms by industry is shown in Table 1.
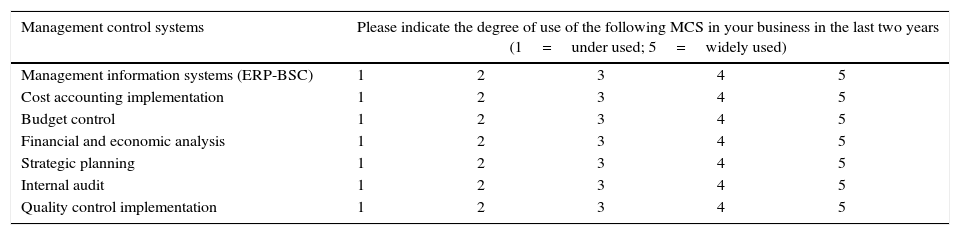
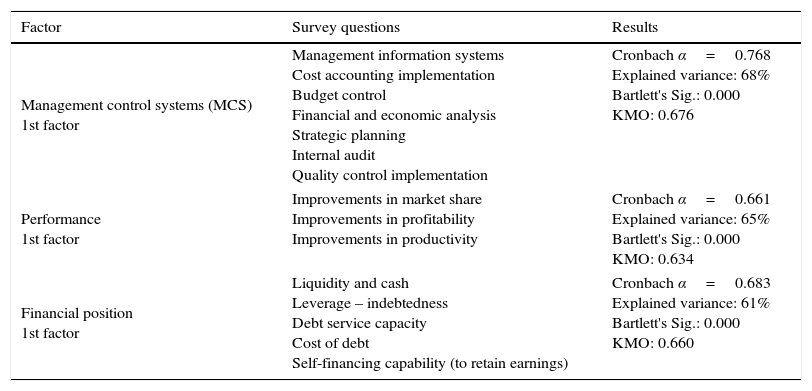
Variables definitionManagement control systems (MCS)To analyze the degree of implementation of MCS requires a measure of subjective perception of the company manager, similar to those used in Choe (1996) or Hoque and James (2000). To this end, the questionnaire included a section that applies a Likert type scale on seven items: management information systems (ERP, balanced scorecard); degree of implementation of cost accounting; budget control; economic and financial analysis; strategic planning; internal audit; and implementation of quality controls. This measure has been used in prior studies such as García-Pérez-de-Lema, Marin, and Martínez (2006) and Esparza, García-Perez-de-Lema, and Duréndez (2009). Subsequently, the responses to a single dimension using factor analysis are reduced. This dimension is assumed to be representative of the perceived by management companies degree of use of MCS. This factor variable explained a 68% of variance and has a Cronbach α=0.768.
PerformanceSME performance is measured using indicators built from the perception of managers regarding the competitive position of their own companies. Faced with the alternative of using indicators from accounting information, this decision is justified for different reasons: if we use accounting information, a number of intangibles, valuable and vital to the competitive success of companies assets are omitted (Camisón, 1997; Kaplan & Norton, 1993), and a time lag occurs between the date of the survey and obtaining accounting information, not officially available until the company publishes its annual accounts. Finally, competitive success is a relative term (AECA, 1988), so the position of the company against the competition is established as one of the key indicators of success or failure.
As a result, the questionnaire entered three Likert questions concerning the increase in market share, profitability and productivity. Later, the responses are reduced by factor analysis to a single representative dimension of perceived performance, with a 65% variance explained and Cronbach α=0.661.
Financial positionIn order to give more robustness to our conclusions, and due to the evolution of the financial situation of the company is closely linked to its performance, we control financial situation when performance is the dependent variable. In this sense, five Likert questions have been included in the questionnaire, concerning the manager's perception regarding the evolution of liquidity and cash position; the level of indebtedness; the ability to refund debt; the cost of debt; and the ability to self-finance the business. These responses are subsequently reduced by a factorial analysis to a single representative dimension of the perceived financial situation of the company. The explained variance of this factor is 61%, while presenting a Cronbach α=0.683.
Table 2 shows the questions that create, by factor analysis, subrogated representative variables of performance, financial position, and intensity of use of management control systems. Main statistics of original variables are reported in Table 3, while Table 4 shows the validation of factorial escalations.
Questionnaire used to factorial analysis of management control systems, performance and financial position.
| Management control systems | Please indicate the degree of use of the following MCS in your business in the last two years (1=under used; 5=widely used) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management information systems (ERP-BSC) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Cost accounting implementation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Budget control | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Financial and economic analysis | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Strategic planning | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Internal audit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Quality control implementation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Performance | Please indicate how has the evolution been of the following aspects of your business in the last two years (1=very unfavorable; 5=very favorable) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improvements in market share | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Improvements in profitability | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Improvements in productivity | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Financial position | Please indicate how has the evolution been of the following aspects of your business in the last two years (1=very unfavorable; 5=very favorable) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquidity and cash | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Leverage – indebtedness | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Debt service capacity | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Cost of debt | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Self-financing capability (to retain earnings) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
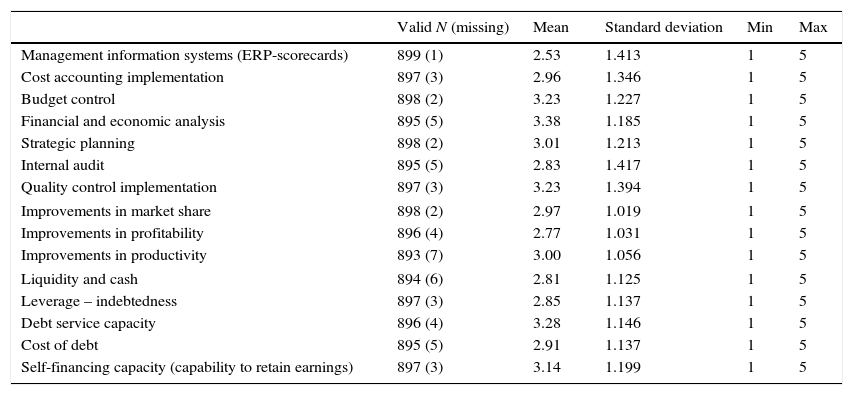
Statistics of original variables.
| Valid N (missing) | Mean | Standard deviation | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management information systems (ERP-scorecards) | 899 (1) | 2.53 | 1.413 | 1 | 5 |
| Cost accounting implementation | 897 (3) | 2.96 | 1.346 | 1 | 5 |
| Budget control | 898 (2) | 3.23 | 1.227 | 1 | 5 |
| Financial and economic analysis | 895 (5) | 3.38 | 1.185 | 1 | 5 |
| Strategic planning | 898 (2) | 3.01 | 1.213 | 1 | 5 |
| Internal audit | 895 (5) | 2.83 | 1.417 | 1 | 5 |
| Quality control implementation | 897 (3) | 3.23 | 1.394 | 1 | 5 |
| Improvements in market share | 898 (2) | 2.97 | 1.019 | 1 | 5 |
| Improvements in profitability | 896 (4) | 2.77 | 1.031 | 1 | 5 |
| Improvements in productivity | 893 (7) | 3.00 | 1.056 | 1 | 5 |
| Liquidity and cash | 894 (6) | 2.81 | 1.125 | 1 | 5 |
| Leverage – indebtedness | 897 (3) | 2.85 | 1.137 | 1 | 5 |
| Debt service capacity | 896 (4) | 3.28 | 1.146 | 1 | 5 |
| Cost of debt | 895 (5) | 2.91 | 1.137 | 1 | 5 |
| Self-financing capacity (capability to retain earnings) | 897 (3) | 3.14 | 1.199 | 1 | 5 |
Scales validation.
| Factor | Survey questions | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Management control systems (MCS) 1st factor | Management information systems Cost accounting implementation Budget control Financial and economic analysis Strategic planning Internal audit Quality control implementation | Cronbach α=0.768 Explained variance: 68% Bartlett's Sig.: 0.000 KMO: 0.676 |
| Performance 1st factor | Improvements in market share Improvements in profitability Improvements in productivity | Cronbach α=0.661 Explained variance: 65% Bartlett's Sig.: 0.000 KMO: 0.634 |
| Financial position 1st factor | Liquidity and cash Leverage – indebtedness Debt service capacity Cost of debt Self-financing capability (to retain earnings) | Cronbach α=0.683 Explained variance: 61% Bartlett's Sig.: 0.000 KMO: 0.660 |
A company was considered a family business if the manager of the company considered in the survey that more than 50% of the capital is in the hands of a family, so that one family control the firm, according to previous literature criteria (Chua et al., 2003; Sharma, Chrisman, & Chua, 1997; Westhead & Cowling, 1998). If the above criterion is not met, the company is regarded as a non-family firm. Thus, the dummy takes value 1 if the company is a family firm and 0 otherwise.
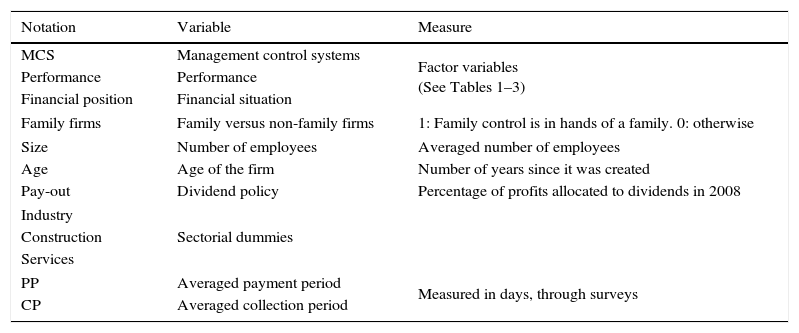
Control variablesSeveral control variables were considered in each model, all of them for the year in which the survey is conducted: company size, measured as the average number of employees; the age of the firm, as the number of years of operations of the company; dividend policy, measured as the percentage of business profits allocated to dividends (pay-out); we also controlled sectorial dummies and, finally, the influence of the averaged collection periods (CP) and payment periods (PP). Financial position is additionally controlled in performance models.
Table 5 summarizes the contents relating to the definition of the variables in the models.
Variables definition.
| Notation | Variable | Measure |
|---|---|---|
| MCS | Management control systems | Factor variables (See Tables 1–3) |
| Performance | Performance | |
| Financial position | Financial situation | |
| Family firms | Family versus non-family firms | 1: Family control is in hands of a family. 0: otherwise |
| Size | Number of employees | Averaged number of employees |
| Age | Age of the firm | Number of years since it was created |
| Pay-out | Dividend policy | Percentage of profits allocated to dividends in 2008 |
| Industry | Sectorial dummies | |
| Construction | ||
| Services | ||
| PP | Averaged payment period | Measured in days, through surveys |
| CP | Averaged collection period | |
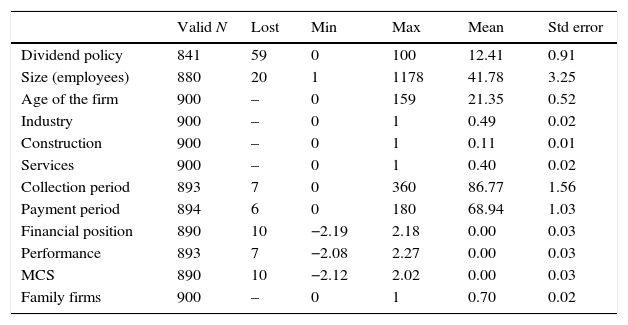
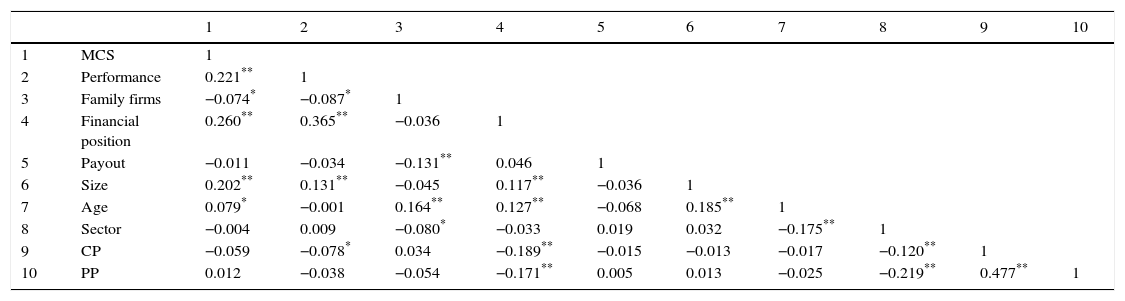
Table 6 summarizes the main descriptive statistics of the variables handled in the OLS regressions that we run to test our hypotheses. Table 7 gathers the bivariate correlations between them.
Descriptives.
| Valid N | Lost | Min | Max | Mean | Std error | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dividend policy | 841 | 59 | 0 | 100 | 12.41 | 0.91 |
| Size (employees) | 880 | 20 | 1 | 1178 | 41.78 | 3.25 |
| Age of the firm | 900 | – | 0 | 159 | 21.35 | 0.52 |
| Industry | 900 | – | 0 | 1 | 0.49 | 0.02 |
| Construction | 900 | – | 0 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| Services | 900 | – | 0 | 1 | 0.40 | 0.02 |
| Collection period | 893 | 7 | 0 | 360 | 86.77 | 1.56 |
| Payment period | 894 | 6 | 0 | 180 | 68.94 | 1.03 |
| Financial position | 890 | 10 | −2.19 | 2.18 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| Performance | 893 | 7 | −2.08 | 2.27 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| MCS | 890 | 10 | −2.12 | 2.02 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| Family firms | 900 | – | 0 | 1 | 0.70 | 0.02 |
Correlations matrix.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MCS | 1 | |||||||||
| 2 | Performance | 0.221** | 1 | ||||||||
| 3 | Family firms | −0.074* | −0.087* | 1 | |||||||
| 4 | Financial position | 0.260** | 0.365** | −0.036 | 1 | ||||||
| 5 | Payout | −0.011 | −0.034 | −0.131** | 0.046 | 1 | |||||
| 6 | Size | 0.202** | 0.131** | −0.045 | 0.117** | −0.036 | 1 | ||||
| 7 | Age | 0.079* | −0.001 | 0.164** | 0.127** | −0.068 | 0.185** | 1 | |||
| 8 | Sector | −0.004 | 0.009 | −0.080* | −0.033 | 0.019 | 0.032 | −0.175** | 1 | ||
| 9 | CP | −0.059 | −0.078* | 0.034 | −0.189** | −0.015 | −0.013 | −0.017 | −0.120** | 1 | |
| 10 | PP | 0.012 | −0.038 | −0.054 | −0.171** | 0.005 | 0.013 | −0.025 | −0.219** | 0.477** | 1 |
Pearson's bivariate correlations. Valid N=795 (missing: 105).
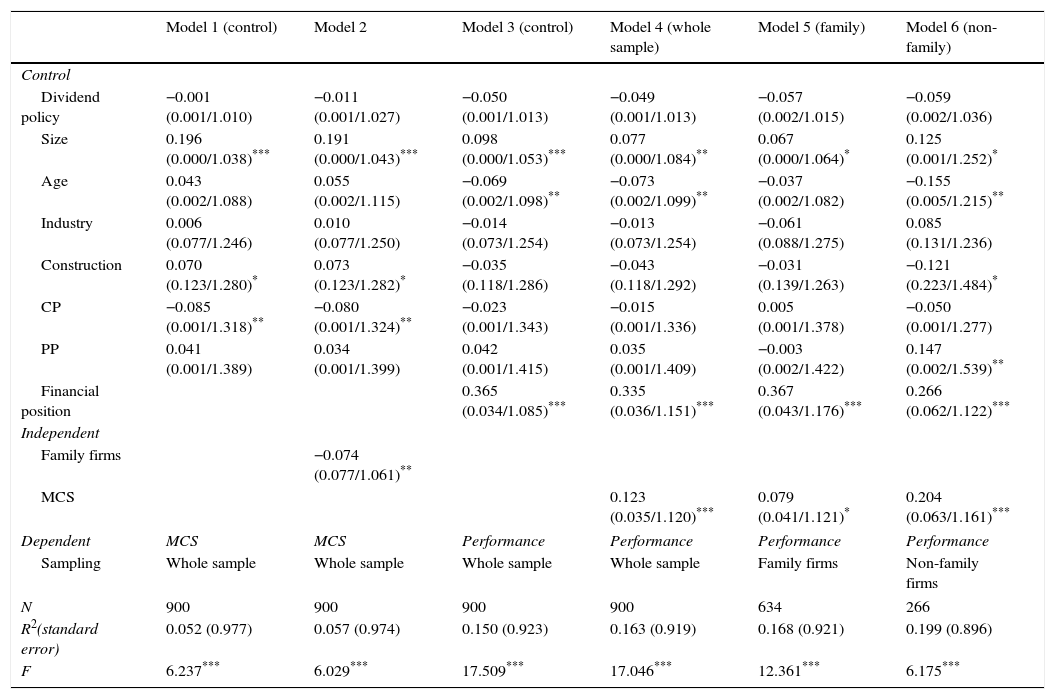
In order to test H1, we checked whether family firms use more or less management control systems than non-family businesses. We run an OLS regression where MCS variable was taken as the dependent variable (see models 1 and 2 in Table 8). A dummy variable named “Family” (family vs non-family firms) was considered as a independent variable, controlling by the use of dividend policy, size, age, sectorial dummies, collection periods, and payment periods. Our results suggest that family businesses use MCS to a lesser extent than non-family businesses.
Regressions.
| Model 1 (control) | Model 2 | Model 3 (control) | Model 4 (whole sample) | Model 5 (family) | Model 6 (non-family) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | ||||||
| Dividend policy | −0.001 (0.001/1.010) | −0.011 (0.001/1.027) | −0.050 (0.001/1.013) | −0.049 (0.001/1.013) | −0.057 (0.002/1.015) | −0.059 (0.002/1.036) |
| Size | 0.196 (0.000/1.038)*** | 0.191 (0.000/1.043)*** | 0.098 (0.000/1.053)*** | 0.077 (0.000/1.084)** | 0.067 (0.000/1.064)* | 0.125 (0.001/1.252)* |
| Age | 0.043 (0.002/1.088) | 0.055 (0.002/1.115) | −0.069 (0.002/1.098)** | −0.073 (0.002/1.099)** | −0.037 (0.002/1.082) | −0.155 (0.005/1.215)** |
| Industry | 0.006 (0.077/1.246) | 0.010 (0.077/1.250) | −0.014 (0.073/1.254) | −0.013 (0.073/1.254) | −0.061 (0.088/1.275) | 0.085 (0.131/1.236) |
| Construction | 0.070 (0.123/1.280)* | 0.073 (0.123/1.282)* | −0.035 (0.118/1.286) | −0.043 (0.118/1.292) | −0.031 (0.139/1.263) | −0.121 (0.223/1.484)* |
| CP | −0.085 (0.001/1.318)** | −0.080 (0.001/1.324)** | −0.023 (0.001/1.343) | −0.015 (0.001/1.336) | 0.005 (0.001/1.378) | −0.050 (0.001/1.277) |
| PP | 0.041 (0.001/1.389) | 0.034 (0.001/1.399) | 0.042 (0.001/1.415) | 0.035 (0.001/1.409) | −0.003 (0.002/1.422) | 0.147 (0.002/1.539)** |
| Financial position | 0.365 (0.034/1.085)*** | 0.335 (0.036/1.151)*** | 0.367 (0.043/1.176)*** | 0.266 (0.062/1.122)*** | ||
| Independent | ||||||
| Family firms | −0.074 (0.077/1.061)** | |||||
| MCS | 0.123 (0.035/1.120)*** | 0.079 (0.041/1.121)* | 0.204 (0.063/1.161)*** | |||
| Dependent | MCS | MCS | Performance | Performance | Performance | Performance |
| Sampling | Whole sample | Whole sample | Whole sample | Whole sample | Family firms | Non-family firms |
| N | 900 | 900 | 900 | 900 | 634 | 266 |
| R2(standard error) | 0.052 (0.977) | 0.057 (0.974) | 0.150 (0.923) | 0.163 (0.919) | 0.168 (0.921) | 0.199 (0.896) |
| F | 6.237*** | 6.029*** | 17.509*** | 17.046*** | 12.361*** | 6.175*** |
Standardized OLS coefficients reported (standard errors/variance inflation factors in parentheses). Dummy “Services” rejected by the systems due to redundant.
Finally, H2 is tested, by analysing the effect of the use of MCS on business performance. To do this, we have built a set of models in Table 8 whose dependent variable is performance, while MCS is computed as an independent variable. We control financial position and the same control variables as above. We ran that regressions to the whole sample (models 3 and 4), where our results suggest that MCS positively affects performance. We complete this study by segmenting our sample in two categories: family firms (model 5) and non-family firms (model 6). Both sub-samples show a positive and significant relationship between the use of MCS and performance. Thus, the positive relationship between use of MCS and performance is confirmed again in both family and non-family businesses.
Concerning control variables, our results suggest that size is a relevant variable to explain the degree of use of management control systems and to improve the performance of companies: larger companies have a more intensive use of MCS and significantly obtain better performances. Then, dimension seems to be an important factor for success. Age seems to be a relevant variable for performance, especially in non-family firms, but it is unable to explain the degree of use of MCS. Unlike the previous case, shorter Collection Periods appear to correlate significantly with the degree of use of MCS, but they do not significantly affect performance. While Payment Periods are significant only in model 6, explaining positively the performance in non-family firms. Meanwhile, construction companies seem to use the MCS more extensively than other sectors, but with a weak significance. No significant differences between industries and service companies were detected. Dividend Policy was not significant for both performance and the degree of use of management control systems, so we cannot confirm whether the pay out impacts on performance or the degree of use of MCS, although their coefficients are negative in every model. Finally, financial position is revealed as one of the most significant variables in order to explain performance in both family and nonfamily firms.
ConclusionsThe aim of this paper was to provide empirical evidence to research literature whether the family and non-family businesses use equally the MCS, as well as to assess the influence of MCS on performance.
Our results support that family businesses use the MCS to a lesser extent than non-family companies, in line with Jorissen et al. (2005), Laitinen (2008), Kotey (2005), Chua et al. (2003) and Perren et al. (1999). Organizational objectives in family firms differ from those in non-family firms, as non-economic goals related to the family itself may be even more essential than the economic goals of the firm (Chua, Chrisman, & Sharma, 1999). Besides, altruism, trust, loyalty or long-term perspective are factors (Schulze, Lubatkin, Dino, & Buchholtz, 2001), quite common in family firms, that might determine the choice of MCS.
Our findings also confirm that the use of the MCS has a positive impact on business performance, in accordance to the majority of the studies (Adler et al., 2000; Dávila, 2000; Laitinen, 2014; Songini & Gnan, 2015). Similarly, our results are in line with those achieved by Schulze, Lubatkin, and Dino (2002) and Lubatkin, Schulze, Ling, and Dino (2005), who could contrast a positive effect of the use of the MCS on corporate performance in family businesses.
This paper contributes to previous literature researching how the family nature of firms affects the use of management control systems (Jayaram, Dixit, & Motwani, 2014). This study provides evidence on how the use of MCS can vary across different types of firms, between family and non-family firms particularly. The study's findings also suggest that the high level of use of MCS positively influence companies’ level of performance. This linkage confirms the Contingency Theory principle that states that the use of MCS can be a source of competitive advantage, influencing performance directly.
In practical terms, our work is also relevant because of the importance of the family business in wealth generation, and it presents contributions of interest to three groups: academics, since it can provide a guidance to new research, as well as providing advances in knowledge of the family business, MCS implementation and performance; entrepreneurs and practitioners, because it may derive some guidelines that can help them to improve the agency relations and evaluate how the MCS affect the competitiveness of enterprises; and policy makers, because it can be used as a reference in such decisions making related to the family and non-family business, promoting the implementation of management control systems.
There are several limitations to our study. Firstly, identification of further control variables should be improved for the study. For example, Gómez Conde, López-Valeiras Sampedro, Ripoll Feliu, and González Sánchez (2013) showed that MCS have a positive influence on the internationalization of food companies, or Lumpkin and Brigham (2011) confirmed the importance of measuring the long-term orientation in the family business as a study variable. Secondly, the study is limited to analysing Spanish companies, specifically in Murcia, so their results might not be generalizable to companies from other regions or countries. Thirdly, because subjective measures of performance, financial condition and intensity in the use of MCS have been used, these results should be interpreted with caution due to the possible existence of bias in the responses to the questionnaire. Fourthly, this study treats family firms as a homogeneous category instead of taking into account the differences that exist between various types of family firms.
Several research extensions can be derived from this article. Firstly, it is necessary to compare the robustness of the findings taking objective measures of performance and financial position as reference variables. Secondly, the expansion of the sample to the international arena would allow the generalization of these conclusions. Thirdly, further studies to validate the approach of resources and capabilities are needed (Gómez Conde et al., 2013). We also share interest with García-Ramos and García-Olalla (2011) in finding some scale to measure the degree of professionalization of the family business, since it could extent the use of MCS in family firms, enhancing their performances. Fourthly, researchers should take into account the heterogeneity of family firms when studying the use of MCS and the performance effects of the choice of MCS.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interests.
Authors acknowledge the funding of this research by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (ECO 2011-29080: the innovation of SMEs in Spain: performance, finance, business cycle and regional growth). This research also benefited from comments and suggestions by participants and reviewers of the III International Symposium of Company Valuation and Family Business held on the 24th and 25th of April 2014, in Almería, Spain. All remaining errors are the authors’ own.